Difference between Anti-Static, Dissipative, Conductive, and Insulative
|
Banned User
|
Difference between Anti-Static, Dissipative, Conductive, and Insulative https://www.gotopac.com/art-esd-resistivity Static Electricity: As the name implies, static electricity is electricity at rest. The electrical charge is the transference of electrons that occurs when there is sliding, rubbing, or separating of a material, which is a generator of electrostatic voltages. For example: plastics, fiber glass, rubber, textiles, ect. Under the right conditions, this induced charge can reach 30,000 to 40,000 volts. When this happens to an insulating material, like plastic, the charge tends to remain in the localized area of contact. This electrostatic voltage may then discharge via an arc or spark when the plastic material comes in contact with a body at a sufficiently different potential, such as a person or microcircuit. If Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) occurs to a person, the results may range anywhere from a mild to a painful shock. Extreme cases of ESD, or Arc Flash, can even result in loss of life. These types of sparks are especially dangerous in environments that may contain flammable liquids, solids or gasses, such as a hospital operating room or explosive device assembly. Some micro-electronic parts can be destroyed or damaged by ESD as low as 20 volts. Since people are prime causes of ESD, they often cause damage to sensitive electronic parts, especially during manufacturing and assembly. The consequences of discharge through an electrical component sensitive to ESD can range from erroneous readings to permanent damage resulting in excessive equipment downtime and costly repair or total part replacement. Electrostatic discharge (ESD): The sudden flow of electricity between two electrically charged objects caused by contact, an electrical short, or dielectric breakdown. A buildup of static electricity can be caused by tribocharging or by electrostatic induction. Anti-Static: Preventing the buildup of static electricity. Reducing static electric charges, as on textiles, waxes, polishes, etc., by retaining enough moisture to provide electrical conduction. Dissipative: The charges flow to ground more slowly and in a somewhat more controlled manner than with conductive materials. Dissipative materials have a surface resistivity equal to or greater than 1 x 105 Ω/sq but less than 1 x 1012 Ω/sq or a volume resistivity equal to or greater than 1 x 104 Ω-cm but less than 1 x 1011 Ω-cm.2 Conductive: With a low electrical resistance, electrons flow easily across the surface or through the bulk of these materials. Charges go to ground or to another conductive object that the material contacts or comes close to. Conductive materials have a surface resistivity less than 1 x 105 Ω/sq or a volume resistivity less than 1 x 104 Ω-cm. Insulative: Insulative materials prevent or limit the flow of electrons across their surface or through their volume. Insulative materials have a high electrical resistance and are difficult to ground. Static charges remain in place on these materials for a very long time. Insulative materials are defined as those having a surface resistivity of at least 1 x 1012 Ω/sq or a volume resistivity of at least 1 x 1011 Ω-cm. https://www.gotopac.com/art-esd-resistivity Have you ever measured how conductive your skin is? |
|
Banned User
|
Does any one have access to accurate surface resistivity measuring equipment. My meter is just standard stuff. Have you any advice about whats hot and whats not? What I have read on the internet has not enlightened me much. I have a rear prob to distinguish between coductive and more so above 10 to the 3.
|
|
Banned User
|
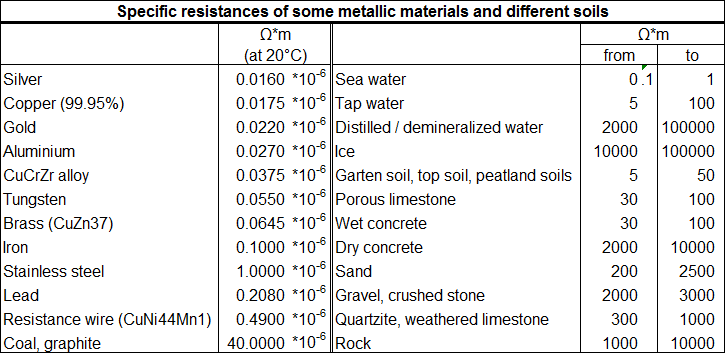 Hope it helps. |
Re: Difference between Anti-Static, Dissipative, Conductive, and Insulative
|
In reply to this post by Plop Plop
I used to get really bad Electrostatic discharge or ESD. I don’t really get it anymore, maybe due to more grounding and knowledge as well as avoidance of emfs. Does that mean people who get really bad ESD might be more conductive than people who don’t??
|
|
Banned User
|
I suspect in EHS their skin is less conductive shorting and more is shorted inside their bodies. This may be facilitated by salts (metal oxides). The mess created by shorting inside us is not easily described scientifically. Becauseoif the mess of wavelengths /voltages and their complexity because of carrier and signal it is probably right to say their effect is best measured in watts and seen as a chaotic disruption of homeostatic equilibrium. We were not designed to suffer from this. More than anything the consequence is likely to be a confusion in our immune system which IDs by charges. It must be freaking the feck out of it at times. The human bio-electric machine uses tiny amps and volts and AC and DC. All of which is designed to to interfere with one another. Now its likely to get confused to hell. Look at health stats if you can find an that are not being actively hidden now.
|
«
Return to ES
|
1 view|%1 views
| Free forum by Nabble | Edit this page |

